Welcome, fellow readers! Today, we’re diving into the fascinating world of PLC commissioning. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out in the field, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to master the art of PLC commissioning and Programming. So, let’s get started!
Understanding PLC Commissioning
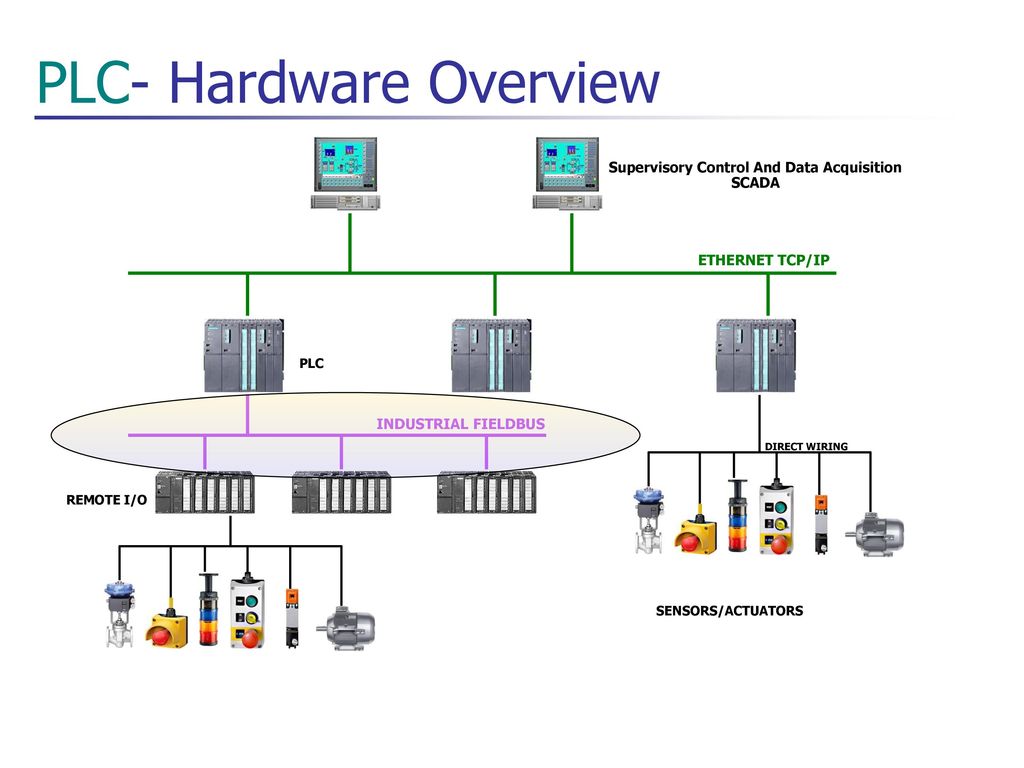
Before we delve into the nitty-gritty details, let’s ensure we’re on the same page regarding PLC commissioning. PLC, short for Programmable Logic Controller, is a vital component in industrial automation. It acts as the brain of a system, controlling and monitoring various processes.
Commissioning a PLC system involves the installation, configuration, and testing of the hardware and software components to ensure the system operates efficiently and reliably. It’s an essential step in bringing automation projects to life.
Step 1: Planning and Preparation
Like any successful endeavor, PLC commissioning begins with meticulous planning and preparation. Here are some key steps to follow:
- Define project requirements: Clearly understand the objectives and requirements of the automation project to ensure accurate commissioning.
- Gather documentation: Collect and review all relevant documentation, including electrical schematics, network diagrams, and user manuals.
- Allocate resources: Determine the necessary human and material resources for the commissioning process.
- Create a commissioning schedule: Develop a detailed timeline and allocate sufficient time for each stage of the commissioning process.
Step 2: Hardware Installation and Configuration
Now that you’ve completed the planning phase, it’s time to move on to the hardware installation and configuration. Here’s what you need to do:
- Mounting and wiring: Properly mount the PLC hardware and connect it to the relevant input and output devices.
- Power up and check connections: Ensure all power connections are secure and double-check the wiring connections.
- Load firmware and configure settings: Install the necessary firmware on the PLC and configure the settings based on the project requirements.
Step 3: Software Development and Testing
Once the hardware is in place, it’s time to focus on software development and testing. Follow these steps:
- Develop the PLC program: Use a programming language like ladder logic or structured text to develop the PLC program that will control the automation processes.
- Download the program: Transfer the developed program to the PLC using the appropriate software and interface.
- Test the program: Perform thorough testing to ensure the PLC program operates as intended. Verify inputs, outputs, and system responses.
Step 4: System Integration and Validation
With the hardware and software components in sync, it’s time to integrate the PLC system with other devices and validate its performance. Consider the following:
- Network configuration: Configure the network connections to enable seamless communication between the PLC and other devices or systems.
- Integrate with HMI/SCADA: Connect the PLC to Human-Machine Interface (HMI) or Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems for effective monitoring and control.
- Validate system performance: Conduct rigorous testing to validate the system’s overall performance, ensuring it meets the desired specifications.
Step 5: Documentation and Handover
As the commissioning process nears completion, it’s crucial to document the work done and prepare for the system handover. Here’s what to focus on:
- Documentation: Compile comprehensive documentation, including operation manuals, maintenance procedures, and troubleshooting guides.
- Training: Provide training to the end-users or operators who will be responsible for maintaining and operating the PLC system.
- System handover: Perform a final review and hand over the commissioned PLC system to the client or end-users.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve now mastered the art of PLC commissioning. By following these steps, you can ensure a smooth and successful commissioning process, leading to optimized automation systems. Remember, PLC commissioning requires attention to detail, patience, and a problem-solving mindset. So, put your skills to the test and enjoy the rewarding journey of PLC commissioning.
Happy commissioning!

